Salmonellosis (Salmonella spp.)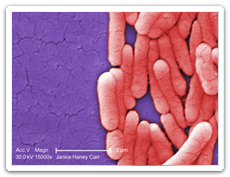
Salmonella organisms are bacteria that cause intestinal illness (salmonellosis) in humans.
Image Content Provider: CDC/Bette Jensen - Photo Credit: Janice Haney Carr
Symptoms
Symptoms usually begin suddenly and can include stomach cramps, diarrhea, fever, nausea and vomiting. Dehydration can also occur, especially in children. Sometimes a person can be infected and have no symptoms or can carry the salmonella organisms for a long period of time. Symptoms typically last 4 to 7 days, and most people recover without treatment. Young children, the elderly and individuals with weakened immune systems such as those who are living with AIDS or cancer, or transplant patients receiving immunosuppressive drugs are more at risk of serious illness.
Causes
Eating contaminated foods, such as raw meat, poultry and eggs that have not been cooked properly, are the most common source of the disease. In addition, raw (unpasteurized) milk and raw milk products, and contaminated water are potential sources of these bacteria. Direct contact with contaminated foods, the feces of infected humans, especially infants with diarrhea, and feces of domestic or wild animals that is not followed by proper hand washing is also a common source of Salmonellosis. Touching raw pet treats such as frozen rodents, that is not followed by proper hand washing can also be a source of the disease. Not washing fresh fruits and vegetables before eating them, as well as not thoroughly cleaning work surfaces used to prepare raw meat and other foods in the kitchen can also expose you to Salmonella. Food can also be contaminated by food handlers who do not thoroughly wash their hands with soap after handling raw meat or after using the bathroom. The disease is more common in summer than in winter.
Treatment
Most people recover without treatment. Your doctor will decide if treatment is necessary in your particular case. People with salmonellosis are usually advised to drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration from diarrhea.
Prevention
Salmonellosis can be prevented by practicing good hand hygiene, especially after using the bathroom, following good food handling practices and by thoroughly cooking beef, pork and poultry before eating.
Manitoba Health Resources
For the Public
For Health Care Providers
- Communicable Disease Management Protocol: Salmonellosis (Nontyphoidal)
(November 2011 with September 2024 updates)
Other Resources
- Canadian Food Inspection Agency - Salmonella
- BC Centre for Disease Control - Salmonella Infection
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention - Salmonella
Communicable Disease
Control (CDC) Health Links – Info Santé |


