Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
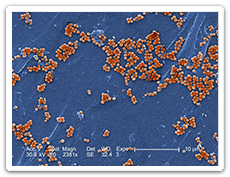 Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a type of Staphylococcus aureus or "staph" bacteria that is resistant to methicillin. Methicillin is an antibiotic used to treat staph infections. Another antibiotic is needed to treat MRSA infection. This infection can cause serious illness if not treated.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a type of Staphylococcus aureus or "staph" bacteria that is resistant to methicillin. Methicillin is an antibiotic used to treat staph infections. Another antibiotic is needed to treat MRSA infection. This infection can cause serious illness if not treated.
Symptoms
Symptoms of MRSA infection vary with its location. Most cases are limited to the skin. If not treated, serious, life-threatening problems such as infection of the bloodstream, bones and/or lungs (for example, pneumonia) may develop.
Causes
Many people carry staph on their hands or in their noses but don’t get ill. Some of these germs may be MRSA. Others are not antibiotic resistant. You may catch MRSA and not get sick. But you can still spread it to others and they can become ill.
MRSA is usually spread by touching, most commonly with the hands, objects soiled with infected bodily fluids. It may sometimes spread through respiratory droplets in the air formed when coughing and sneezing. You can also infect yourself through an open wound, burns, or intravenous catheters or drainage tubes.
Treatment
MRSA infection is treated depending on how serious it is. Your health care provider may drain your wound or prescribe antibiotics other than methicillin. For mild skin infections, you may be given a skin ointment and antibiotic soap.
Prevention
MRSA infection may be prevented by practicing good hand hygiene. Do not touch without protection other people’s wounds or bandages. Always clean and cover with a bandage your own cuts and scrapes until they heal. Finally, do not shar personal items, such as towels or razors.
Manitoba Health Resources
For the Public
For Health Care Providers
- Manitoba Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Antibiotic Resistant Organisms (AROs)
(January 2007) - Admission Screening Statement for MRSA and VRE for Acute Care Facilities and Surgical Centres
(January 2007)
Other Resources
- HealthLinkBC – Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Overview
- Public Health Agency of Canada – Fact Sheet – Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Communicable Disease
Control (CDC) Health Links – Info Santé |


